배관 균열형태와 밸브개폐에 따른 음향방출신호 및 진동신호의 특징분석
‡ Recommended by Editor Soo Il Lee
© The Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering
Abstract
Machinery typically consists of numerous pipes and valves. In particular, Pipes in power plant, are prone to defects owing to high-temperature, high-pressure steam. Such defects may result in reduced efficiency and increased risk of accidents due to fluid leakage. In this study, an experimental model used pipe used in heat exchangers to detect early defects in pipes. The classification performance of the vibration and acoustic emission signals was evaluated; specifically, the classification performance of acoustic emission signals before and after the pre-processing was evaluated. The characteristics used for classification were selected using three discriminative features by applying a GA(genetic algorithm), and the classification performance was evaluated using a support vector machine. The results of the study are expected to be the basis for early detection of pipe defects.
Keywords:
Pipe Cracking, Vibration Signal, Acoustic Emission, Feature Analysis키워드:
배관 균열, 진동 신호, 음향방출, 특징 분석1. 서 론
기계설비는 기계적 결함, 작동 오류, 사고 및 자연재해 등에 의해 구동정지가 일어난다. 이 같은 구동 정지에 의해 기계설비의 중단 될 시 큰 비용을 초래하게 된다. 이처럼 중단 시에 많은 비용이 들지만 중단 없이 설비에 대한 신뢰성을 향상시키기는 어렵다(1).
기계설비에는 복잡하고, 다양하게 배관이 사용되고 있다(2). 이러한 기계설비 내의 배관은 유체의 이동수단 역할(3)로 사용되며, 특히 플랜트 내의 배관은 고온, 고압의 증기로 인해 배관결함 가능성이 있다(4). 이 같은 배관결함으로 인한 누설 시 효율성 감소 및 화재사고로 인한 인명피해가 있을 수 있다.
플랜트 내의 배관은 내부응력, 부식, 충격 등으로 인해 배관의 균열이 발생 할 수 있다. 배관의 결함 형태로는 부식 결함, 기계적 결함과 같은 다양한 결함이 존재한다(5). 또한 용접에 의한 잔류응력 등 여러 형태의 응력에 지배를 받으며, 이러한 원인들로 인해 수평 및 수직방향 균열로 나타나게 된다.
플랜트 내의 배관에는 많은 밸브들이 존재하며(6), 밸브유체누설로 인한 안전사고 및 에너지손실이 생긴다. 하나의 밸브의 누설량은 적지만, 플랜트 내에는 많은 밸브들이 존재하므로 이러한 많은 밸브들이 함께 누설 된다면 또 다른 효율성 문제를 일으킨다.
사고 및 인명피해 효율성 감소에 대한 문제를 보완하기 위해 누설이 발생하는 밸브와 배관결함을 조기에 탐지하는 연구가 활발히 진행되고 있다. 이러한 탐지방법에는 가속도 센서를 이용한 진동측정과 초음파, 방사선, 음향방출법과 같은 비파괴 검사가 대표적이다(7).
이 연구에서는 가속도 센서와 음향방출센서를 사용하였으며, 가속도 센서는 설비기기의 충격, 진동과 같은 동적인 힘을 측정하며 기기의 운동 상태를 상세하게 감지 할 수 있다. 음향방출신호는 배관 내의 유체 유동에 의해 구조물에 표면파로 생성되어 전파되는 것이며, 일반적인 구조물에서 유체의 유동은 압력으로 변환되며 이 압력이 소리를 발생시키는데 이를 음향방출신호라고 한다(5). 이러한 음향방출신호는 실시간으로 모니터링이 가능하며, 센서 한 개로 넓은 영역을 감지 할 수 있다. 하지만 음향방출신호의 경우 잡음이 많이 포함되어 있는 단점이 있기 때문에, 원 신호를 이용하여 분석하기는 쉽지 않다. 따라서 음향방출센서의 경우 envelope(포락) 전처리의 일종인 Hilbert transform(힐버트 변환)을 이용하여 전처리 전/후 데이터를 비교하였다.
일반적으로 배관 운용 시 넓은 주파수 대역에 주파수 신호가 존재한다. 음향방출센서로 고주파신호를 측정하며, 가속도 센서로 음향방출센서에 비해 저주파인 진동신호를 수신한다(7). 따라서 가속도 센서와, 음향방출 센서를 모두 사용함으로써 보다 넓은 대역의 진동을 모두 확인 할 수 있다.
이 연구에서는 정상배관과 다양한 균열을 모사하기 위해 수평방향, 수직방향 균열 배관을 사용하였으며, 정상배관과 균열배관, 밸브의 개폐여부에 따라 진동신호와 전처리 전· 후의 음향방출신호를 비교분석함으로써 배관결함 조기 진단 가능성을 확인하고자 한다.
2. 실 험
2.1 실험 모델
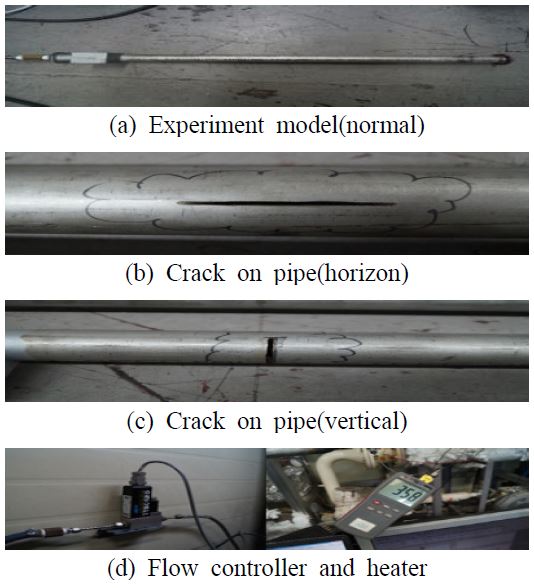
실험 모델로는 열교환기 구성부품인 배관을 사용했으며, 정상상태의 배관, 수평방향, 수직방향 균열을 모사한 배관을 사용하였다. 각 Fig. 1의 (a) ~ (c)에 균열을 모사한 배관을 나타내었다. 수평방향으로 가로 50 mm 세로 3 mm, 수직방향으로 가로 3 mm, 세로 50 mm의 균열을 낸 배관을 사용했으며, Fig. 1(d)의 heater와 공기 압축기를 이용해 60 ℃, 30 m3/min로 설정하였다.
2.2 실험 방법
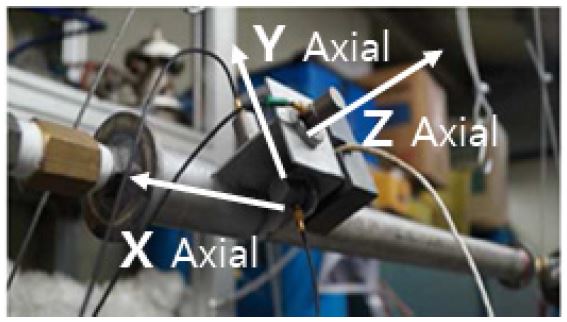
실험 case는 밸브 개폐, 정상상태, 수평방향, 수직방향 균열 형태에 따라 총 5가지로 실험을 진행했으며, Table 1에 나타내었다. 데이터 취득형태는 Fig. 2와 같이 X, Y, Z에 가속도 센서를 부착하였고, Z축에 음향방출센서를 부착하여 각각 진동신호와 음향방출신호를 30초 동안 취득하였다.
2.3 특징 추출 및 분류
진동 및 음향방출신호를 취득하여 시간, 엔트로피, 주파수영역의 총 30가지 특징 값에 대해 취득된 신호를 비교 분석하였다. 특징 값은 Fig. 3에 정리하여 나타내었다.
시간, 엔트로피, 주파수 영역의 총 30가지 특징 중 Table 1의 5가지 케이스를 가장 잘 분류해 줄 수 있는 특징 3가지를 GA(genetic algorithm)를 이용하여 특징을 선택하였다. GA 기반 특징 선택은 각 클래스 내의 밀도와 클래스 간의 평균거리를 목적 함수로 설정하여 정해진 세대수 만큼 반복하여 최상의 적응도를 갖는 특징 값을 이용하여 최적화 하였다(8).
GA를 이용하여 선택된 특징 3가지를 X, Y, Z 축으로 나타내어 Table 2의 5가지 케이스를 3차원 평면에 나타내었으며, 기계학습의 알고리듬 중 하나인 SVM(support vector machine)을 사용하여 분류성능을 평가하였다(8). SVM은 클래스 사이의 평면을 생성하여, 클래스와 평면사이의 거리를 통해 분류성능을 평가하는 기법이다. 이 논문에서 취득한 데이터의 2/3는 training데이터로 사용되었으며, 1/3은 test데이터로 사용하였다(9). 1/3의 test데이터를 이용하여 각 case의 분류성능 및 전체 case의 분류성능 %를 확인하였다.
3. 결 과
3.1 진동신호의 분류결과
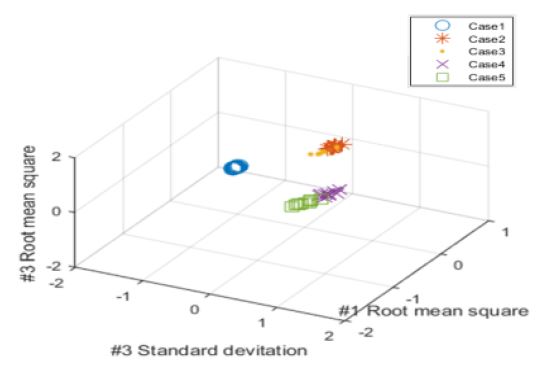
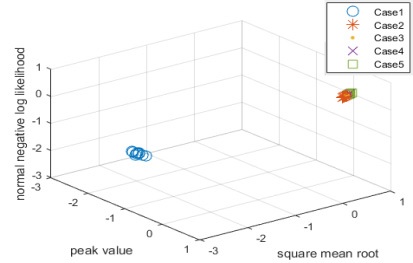
Fig. 4는 진동신호의 분류결과이며, case 1은 정상, case 2, 3은 수평방향 균열, case 4, 5는 수직방향 균열을 나타내며, case 2, 4의 경우 밸브가 열린 상태, case 4, 5의 경우 밸브가 닫힌 상태를 나타낸다. 5가지 case 모두에 대해 분류성능이 75 %가 나왔으며, 정상과 균열배관, 밸브 개폐에 따라 분류가 되었음을 확인 할 수 있다.
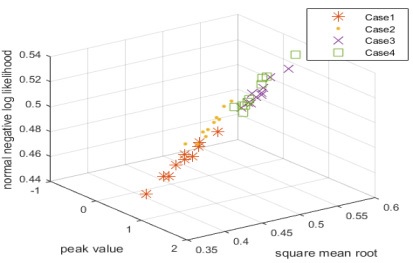
Fig. 5는 정상을 제외한 나머지 4개의 case에 대한 분류 결과이며 분류성능은 69 %로 확인되었다.
3.2 전처리 전의 음향방출신호 분류결과
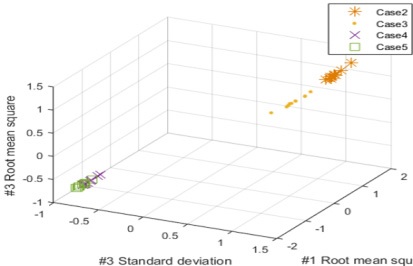
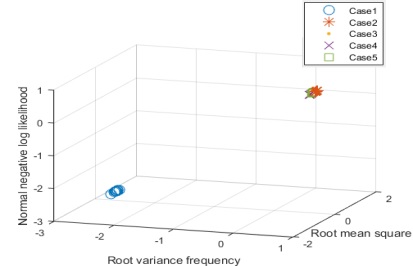
Fig. 6은 전처리 전의 음향방출신호의 5가지 case 모두에 대한 분류 결과이다. 분류 결과 분류성능은 81 %가 나왔으며, 정상과 균열형태에 따라는 분류가 되었음을 확인 할 수 있다.
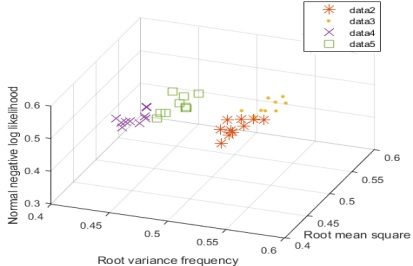
Fig. 7은 정상상태를 제외한 나머지 4개의 case에 대한 분류 결과이며, 분류성능은 87 %로 확인되었다. 균열형태에 따라는 분류가 되었지만, 수직방향 균열의 밸브 개폐에 따라는 분류가 되지 않았음을 확인 할 수 있다.
3.3 전처리 후의 음향방출신호 분류결과
Fig. 8은 전처리 후의 음향방출신호의 분류 결과이며 분류성능은 87 %로 나왔다. 정상과 4개의 case는 분류가 되었지만, 균열형태와 밸브개폐에 따라는 분류가 되지 않았음을 확인 할 수 있다.
Fig. 9는 정상상태를 제외한 4개의 case의 분류결과이며, 분류성능은 100 %로 확인되었다. 수평방향, 수직방향 균열, 밸브 개폐에 따라 분류가 되었음을 확인 할 수 있다. 또한 전처리 전과 다르게 수직방향 균열에서 밸브개폐에 따라도 분류가 되었음을 확인 할 수 있다.
Table 2에 Figs. 4 ~ 11의 분류성능을 요약하여 나타내었다. Classification 5 case는 정상, 수평방향균열, 수직방향균열 배관 전체에 대한 분류성능이며, classification 4 case는 수평, 수직방향균열 배관의 분류성능, total은 4, 5 case 분류성능의 평균을 나타내었다.
4. 결 론
이 논문에서는 정상배관, 수평, 수직방향 균열배관을 사용했으며, 진동신호와 음향방출신호를 취득하여 균열형태와 밸브개폐에 따라 총 5가지 case로 나누어 실험을 진행하였다.
그 결과 진동신호의 경우 평균적으로 분류성능은 72 %, 음향방출 원 신호의 경우 86 % 전처리 후의 음향방출신호의 경우 94 %로 확인되었다.
이 연구의 균열배관에는 진동신호보다 음향방출 신호가 분류성능이 뛰어났다. 이는 배관의 진동은 전대역이 진동하므로 측정대역이 넓은 음향방출신호가 더 많은 결함신호를 포함하고 있기 때문이라고 판단된다.
또한 envelope 전처리를 수행한 음향방출신호가 전처리 전의 음향방출신호보다 분류성능이 우수함을 확인하였다. 이는 음향방출센서의 경우 잡음을 많이 포함하고 있기 때문이라고 판단된다.
이 연구의 실험모델인 열교환기 배관으로 정상배관 및 결함배관과 밸브개폐에 따라 다른 특성을 확인하였으며, 이러한 연구가 배관 조기결함 탐지에 크게 기여할 것이라 판단된다.
Acknowledgments
이 연구는 “자동예측 진단 기술 개발(한국수력원자력 중앙연구소)”의 지원(L17S086000)으로 수행되었으며, 관계자 여러분께 감사드립니다.
References
-
Kim, J. M., Ahn, B. H., Lee, J. M., Yu, H. T. and Choi, B. K., 2017, Feature Analysis of Vibration and Acoustic Emission According to Pipe Cracking and Valve Opening/Closing, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, Vol. 27, No. 7, pp. 857~862.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/KSNVE.2017.27.7.857]

- Jeon, B. C., Jung, J. H. and Youn, B. D., 2013, Anomaly Diagnostics for Rotor System using Statistical Analysis of Vibration Signal, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, Vol. 23, No. 10, pp. 831~832.
-
Ha, J. S. and Lee, B. Y., 2013, A Study on the Steam Hammering Characteristics by Sudden Closure of Main Stop Valve in the Main Steam Piping System of a Power Plant, Journal of the Korean Institute of Gas, Vol. 17, No. 2, pp. 70~77.
[https://doi.org/10.7842/kigas.2013.17.2.70]

-
Kim, S. O., Jeon, H. S., Son, K. S., Chae, G. S. and Park, J. W., 2015, Steam Leak Detection Method in a Pipeline Using Histogram Analysis, Journal of the Korean Society for Nondestructive Testing, Vol. 35, No. 5, pp. 307~313.
[https://doi.org/10.7779/JKSNT.2015.35.5.307]

- Oh, K. H., Yeom, G. J. and Kim, W. S., 2014, Status of Gas Piping Defect Assessment, Transactions of the Korean Society of Mechanical Engineers, Vol. 54, No. 1, pp. 38~42.
- Lee, S. G., Km, D. W., Kim, Y. S., Park, J. H. and Jeong, H. H., 2009, Study on Statistical Analysis of Measured Fluid Leakage Data and Estimation of the Leakage Rate for Power Plant Valve, Journal of the Korean Society for Power System Engineering, Vol. 13, No. 5, pp. 59~66.
- Kim, Y. H., Kim, J. H., Song, B. M., Lee, J. H. and Cho, Y. H., 2009, A Study on the Leakage Characteristic Evaluation of High Temperature and Pressure Pipeline at Nuclear Power Plants Using the Acoustic Emission Technique, Journal of the Korean Society for Nondestructive Testing, Vol. 29, No. 5, pp. 466~472.
-
Kim, H. J., Ahn, B. H., Park D. H. and Choi, B. K., 2017, Feature Analysis for Fault Diagnosis According to Gearbox Failure, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, Vol. 27, No. 3, pp. 312~317.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/KSNVE.2017.27.3.312]

-
Ahn, B. H., Kim, Y. H., Lee, J. M., Lee, J. H. and Choi, B. K., 2014, Signal Processing Technology for Rotating Machinery Fault Signal Diagnosis, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, Vol. 24, No. 7, pp. 555~561.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/KSNVE.2014.24.7.555]


Yun O Choi is unified Bachelor's course degrees at the Department of Energy and Mechanical Engineering at Gyeongsang National University in Korea. Areas of research are dynamic analysis of the shaft through FEM analysis and measurement for diagnosis.

Jeong Min Kim is unified Bachelor's course degrees at the Department of Energy and Mechanical Engineering at Gyeongsang National University in Korea. Areas of research are dynamic analysis of the shaft through FEM analysis and measurement for diagnosis.

Byung Hyun Ahn is unified doctor's course degrees at the Department of Energy and Mechanical Engineering at Gyeongsang National University in Korea. Areas of research are dynamic analysis of the shaft through FEM analysis and measurement for diagnosis.

Byeong Keun Choi is a Professor at the Department of Energy and Mechanical Engineering at Gyeongsang National University in Korea. He received his Ph.D. degrees in Mechanical Engineering from Pukyong National University, Korea, in 1999. Dr. Choi worked at Arizona State University as an Academic Professional from 1999 to 2002. Dr. Choi’s research interests include vibration analysis and optimum design of rotating machinery, machine diagnosis and prognosis and acoustic emission. He is listed in Who's Who in the World, among others.