바닥충격음 연구현황 및 전망
© The Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering
Abstract
Since the last 30 years, there have been various studies conducted on different topics related to floor impact sound. In this study, the papers and proceedings presented at KSNVE (The Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering) for the past 30 years are sorted as per the topics, and the results were analyzed. The main subjects of these floor impact sound papers were floor impact sound isolation system, including the resilient materials, and papers on measurement and evaluation methods and prediction. Research on the prediction of floor impact sound has been conducted since 2005. Recently, research has been conducted on improving the floor impact sound isolation performance of existing apartment buildings or remodeling houses. For the slabs of apartment buildings, establishing a method for predicting the floor impact sound is imperative. It is urgent to issue international standards for the SNQ and classification scheme of rubber ball impact sound. Furthermore, adding the rubber ball impact sound measurement method as part of international standards is necessary. It is considered that the simple measurement method of rubber ball impact sound can be useful for the investigation of basic data for the development of quality control techniques in this field.
Keywords:
Floor Impact Sound, Review of Previous Studies키워드:
바닥충격음, 연구 리뷰1. 서 론
동주택 보급이 증가하고 우리나라의 주요한 주거 형태로 자리 잡음에 따라, 바닥충격음은 관련 민원과 관심은 지속적으로 증가되고 있다. 1990년 말부터 공동주택에서 발생되는 바닥충격음을 저감하기 위한 연구가 본격적으로 시작되었다. 이후 2000년대 부터 완충재 개발, 측정·평가 방법 연구 등 다양한 연구 결과가 발표되고 있다. 바닥충격음 관련 연구 결과는 한국소음진동공학회에서 가장 많이 발표되고 있으며, 최근까지 다양한 연구결과가 지속적으로 활발히 논의되고 있다. 최근에는 기존 주택의 바닥충격음 차단성능 개선을 위한 연구, 바닥충격음 관련 제도 개선 및 표준 기반 확충 등이 이루어지고 있다.
바닥충격음 관련 연구는 약 30여 년 동안 다양한 주제로 연구가 수행되었으나, 아직도 바닥충격음 관련 민원과 불만이 제기되고 있다. 이에 이 연구에서는 지난 30여 년 동안 한국소음진동공학회에서 발표된 논문과 학술발표를 바닥충격음 관련 제도, 표준 개선 등의 분류로 구분하고 세부 주제별로 비교하고자 한다. 이를 통해 과거 수행된 바닥충격음 연구 분야를 확인하고 그간 부족했고 시급하게 필요한 바닥충격음 연구 분야를 도출하여 제시하고자 한다.
2. 제도 및 표준 기반
한국환경공단의 층간소음 이웃사이센터 콜센터와 온라인으로 접수된 층간소음 관련 상담은 2017년 22849건으로 2012년 개소된 이후 지속적으로 증가하고 있다(1). 바닥충격음 관련 제도 및 기준이 시행되고 여러 가지 바닥충격음 저감을 위한 연구가 수행되고 있지만, 층간소음 관련 민원은 줄어들지 않고 있다. 이러한 원인을 분석하기 위해 우선 바닥충격음 관련 제도 시행과 개선, 바닥충격음 관련 표준 기반에 대하여 검토하였다. Table 1은 바닥충격음 관련 국가표준 제·개정과 제도 시행에 대한 내용을 시간순서에 따라 정리한 것이다.
바닥충격음 저감 등을 위한 연구, 개발을 위해서는 관련 표준기반 구축이 선행되어야 한다. 바닥충격음 차단성능을 측정하기 위한 표준은 1996년 최초로 제정(2)되었으며, 2001년 경량·중량충격음 측정방법으로 각각 분리하여 개정(3,4)되었다. 2012년에는 표준 중량 충격원으로 고무공 충격원이 KS F 2810-2에 추가로 규정되었다. 이와 같은 표준 제·개정을 바탕으로 바닥충격음 차단구조와 관련 기준 등에 대한 연구가 시작되었다.
바닥충격음 관련 제도는 2002년 주택건설기준 등에 관한 규정 개정안에 경량과 중량충격음에 대한 기준이 반영되었으며, 공동주택 바닥충격음 차단구조 인정 및 관리 기준이 2005년부터 시행되었다. 이후 2014년에는 해당 고시안이 고무공 충격원에 대한 내용과 현장과 실험실 성능 차이를 최소화하기 위한 내용이 추가되었다. 또한 2014년에는 소규모 공동주택, 고시원과 오피스텔에도 층간소음 기준을 적용하도록 하였다. 우리나라는 바닥충격음 관련 기준을 의무화한 유일한 국가이며, 이는 바닥충격음 관련 민원이 많고 폭력, 살인과 같은 사회적 문제로 표출되기 때문으로 판단된다.
Table 2는 바닥충격음 관련 ISO 국제표준과 KS 표준을 비교한 것이다. 바닥충격음 관련 국제표준 구성은 Table 2와 같이 연구개발 단계 등을 고려하여 마감재와 완충재의 물성 측정에서부터, 시험방법, 단일수치평가량 평가방법, 예측방법과 평가등급으로 구분할 수 있다. 시험방법은 시험의 정확도 등급과 시험 환경에 따라 시험실 측정방법(accuracy grade 1-precision method), 현장 측정방법(accuracy grade 2-engineering method)과 간이 측정방법(accuracy grade 3-survey method)로 구성된다. 간이 측정 방법은 시험실과 현장 측정 방법을 간략화한 방법으로 현장에서의 품질관리 시험, 최종 제품의 개략적인 성능 파악 등에 활용할 수 있을 것으로 판단된다. ISO 국제표준에는 경량충격음 예측에 대한 표준(ISO 12354-2)(5)과 예측시 입력량으로 필요한 물성 등을 측정하는 방법(ISO 10848-1 ~ 4)(6 ~ 9)이 규정되어 있으며, 최근에는 주거용 건축물의 음향 성능(경량충격음, 공기전달음, 외피차음성능, 설비소음 등)에 대한 평가 등급과 표시 방법에 대한 표준 제정(10)을 추진하고 있다. 그러나 중량충격음은 시험실과 현장 측정방법에만 고무공 충격원을 활용하는 방법이 ISO 표준에 반영되어 있으며, 고무공 충격음 단일 수치 평가 방법의 국제표준화가 추진되고 있다.
KS의 경우 뱅머신과 고무공 충격원을 활용하는 중량충격음에 대한 내용은 표준화되어 있지만, 간이 측정방법, 예측방법과 평가 등급에 대한 내용은 부족한 실정이다. 위의 내용에 대한 ISO 표준을 부합화한 KS 제·개정 추진이 필요하며, 이때 우리나라의 상황과 기술 여건 등 제반 요소를 고려하여 선별적으로 부합화하거나 우리 고유의 기술 등을 반영하여 표준화하는 방안을 고려할 수 있다. 중량충격음 측정·평가 기술은 우리나라가 유럽, 북미의 국가들보다 먼저 추진하고 있어 우리의 중량충격음 측정·평가 방법과 등급(고무공 충격원 기반)을 국제표준으로 추진하고 있다.
중량충격음 예측 기술의 경우 우리나라에서 수행한 연구 결과를 종합하고 표준안을 수립하여 국제표준으로 제안할 수 있을 것으로 판단된다. 또한 중량충격음 예측 기술은 바닥충격음 저감기술 개발과 성능 검증 등에 효과적으로 사용할 수 있으며, 다양한 공동주택 구조의 최적화에도 활용할 수 있다. 이를 바탕으로 현장에서의 품질관리 요인 도출과 품질관리 기법 개발, 활용에도 효과적으로 활용할 수 있다.
3. 바닥충격음 관련 연구 현황
한국소음진동공학회에서는 1990년 부터 바닥충격음 연구 결과 발표가 시작되었으며(11), 2000년 부터 활발하게 발표되었다. 바닥충격음 관련 연구 논문은 2002년 발표된 이후 지속적으로 발표되고 있다.
Fig. 1은 한국소음진동공학회에 발표된 바닥충격음 관련 연구 논문과 학술발표건수를 연도별로 정리하고, Table 1의 바닥충격음 관련 주요 이슈와 함께 정리한 것이다. 2019년 3월 현재 한국소음진동공학회에 발표된 바닥충격음 연구 논문은 40편이며, 327건의 학술발표가 발표되었다(2019년 춘계학술대회 포함). 바닥충격음 관련 연구 발표는 2001년 KS F 2810-1, 2 개정 전후로 급격히 증가되었으며, 국토교통부의 바닥충격음 관련 법제화에 따라 저감구조 개발 등 다양한 연구가 활발하게 추진, 발표된 것으로 판단된다. 2005년 바닥충격음 차단구조 인정제도 시행 이후 다소 감소하였으며, 2007년 연구 발표가 증가되었지만, 이후 다시 감소하였다. 이는 바닥충격음 차단구조 인정제도와 관련 시장이 완충재를 포함한 차단구조로 안정화되었기 때문으로 판단된다. 2012년 관련 연구는 고무공 충격원을 포함하는 KS F 2810-2 개정과 시험실과 현장의 차이를 줄이기 위한 국토부 고시안 개정으로 다시 증가하였으며 현재까지 지속적으로 연구결과가 발표되고 있다. 2014년에는 환경부의 층간소음 배상 및 수인한도 기준 수립과 기존 공동주택과 리모델링 공동주택에서의 바닥충격음 차단성능 향상을 위한 연구 요구로 1990년 이후 가장 많은 연구결과가 발표되고 있다. 연구 논문 발표는 학술발표 건수의 약 12 % 정도 수준이었으며, 학술발표와 1년 ~ 2년 정도 차이로 유사한 경향을 갖는 것으로 나타났다. 이는 연구과정의 결과를 학술발표하고 종합적으로 정리하여 연구 논문으로 발표하기 때문으로 사료된다.
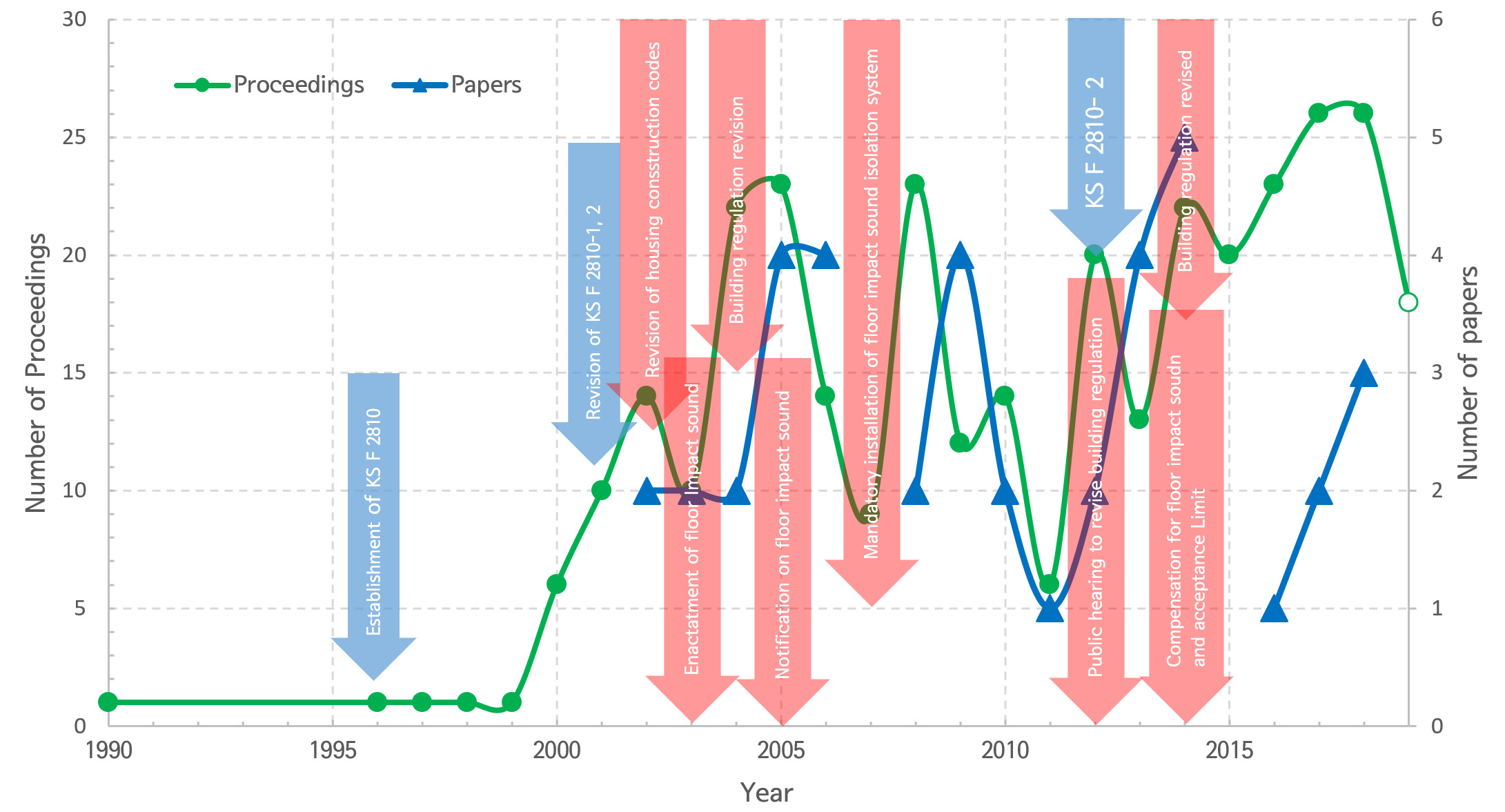
Number of papers and proceedings and major issue related to floor impact sound from the 1990s to at present sorted by year
Table 3은 1990년 이후 발표된 학술발표와 논문을 1저자의 소속기관별로 구분하여 정리한 것이다. 바닥충격음 관련 학술발표는 교육기관의 비중이 높기는 하지만 산/학/연 모두 활발하게 발표하고 있지만, 논문은 학/연 중심으로 게재되고 있다. 바닥충격음 연구는 다양한 저감구조, 측정, 평가 방법 개발 등에 관한 것으로 산업계의 경우 연구 결과에 대한 지적재산권 문제, 연구결과 공표에 대한 부담 등도 영향을 미치는 것으로 사료된다.
3.1 바닥충격음 논문 게재 현황
한국소음진동공학회에 발표된 40편의 바닥충격음 관련 논문은 바닥충격음 저감 대책, 측정·평가 방법, 예측과 기타 주제로 세부 주제별로 분류할 수 있다. Table 4는 40편의 논문을 주제별로 구분하고 정리한 것이다. Table 4에서와 같이 저감구조에 대한 논문은 약 35 %, 측정‧평가에 대한 논문은 32.5 %, 바닥충격음 예측에 대한 논문은 22.5 %였으며, 층간소음에 대한 설문조사와 청감평가 등 기타 주제에 대한 논문은 10 %였다.
바닥충격음 저감구조에 대한 연구는 저감방안별 성능평가를 바탕(12)으로 다양한 저감 방안과 천장과 벽을 통한 저감 방안(13)이 연구되었다. 우리나라의 바닥충격음 저감구조는 대부분 완충재를 사용한 뜬바닥 구조를 기반으로 하고 있으며, 완충재 개선을 위한 물성개선 및 바닥충격음 레벨에의 영향(14 ~ 17), 공동주택 평면구조와 완충재의 영향 등(18)에 대한 논문이 게재되었다. 또한 바닥충격 에너지를 저감시키기 위한 제진재가 적용된 바닥구조에 대한 연구(19)도 수행되었다, 완충재 위쪽에 시공되는 경량기포 콘크리트 개선에 대한 연구결과(20)와 슬래브와 상부 바닥구조가 일체된 저감 구조(21)에 대한 연구도 수행되었으며, 일부 연구 결과는 실제 시공까지 반영된 것으로 알려져 있다. 이와 같은 바닥충격음 저감재가 적용된 공동주택의 중량충격음 특성과 기준 만족 정도에 대한 현장 조사 결과(22)가 발표되었다. 최근에는 기존 공동주택 및 리모델링시 바닥충격음 저감을 위한 천장, 마감재 및 건식구조에 대한 관심이 증가되고 있으며, 이에 대한 연구결과(23 ~ 25)는 2002년 부터 발표되고 있다.
실제 공동주택에서 발생되는 충격음을 효과적으로 저감하기 위해서는 실제 충격원과 가장 유사한 충격원을 측정하고 거주자가 느끼는 거슬림 등 주관적 반응과 상관성이 가장 높은 평가 방법으로 평가하는 것이 효과적이다. 이와 관련된 바닥충격음 측정‧평가 방법에 대한 연구도 활발하게 수행되고 있다. 충격원에 대한 연구가 가장 먼저 수행되었으며, 실제 충격원에 대한 정의(26,27)와 임팩트 볼(rubber ball)과 실충격원 특성 비교에 대한 연구 결과(28,29)가 발표되었다. 이후 바닥충격음 측정시 수음실의 잔향시간과 음장 특성이 바닥충격음 레벨에 미치는 영향에 대한 조사와 개선 방법에 대한 결과(30 ~ 33)가 제시되었다. 청감실험 결과를 기반으로 한 바닥충격음과 공동주택의 복합 생활소음 평가 등급과 평가 방법 개선에 대한 연구 결과(34,35)와 함께 슬래브 구조 자체의 충격음과 진동 특성 평가에 대한 연구(36,37)도 수행되었다. 바닥충격음 레벨 측정, 평가 방법과 함께 완충재(38)와 모르타르(39)와 같은 공동주택 바닥구조 구성 재료별 성능 측정 방법 개선을 위한 연구가 수행되었으며, 일부 완충재에 대한 연구결과는 제도 개선과도 관련된 것으로 판단된다.
바닥충격음 차단 예측은 바닥충격음 저감 성능이 우수한 구조 설계, 보수‧보강 방법 개발과 향후 현장에서의 시공 품질 관리 기법 개발 등 다양한 분야에서 활용될 수 있다. 경량충격음의 예측 방법은 유럽 국가를 중심으로 예측 방법이 개발되고 표준화(40)되었다. 중량충격음 예측에 대한 연구 결과는 2003년 부터 논문으로 발표되었으며, 초기에는 충격원 가진시 구조체로 전달되는 진동량 측정을 통한 전달경로와 진동 전달률 연구(41,42)로 시작되었다. 이후 중량충격음 예측을 위해 유한요소법을 이용한 2차원 바닥 충격진동 해석에 대한 연구(43)와 공동주택 축소 모형을 이용한 연구(44)와 같이 다양한 이론적, 실험적 방법을 활용한 연구가 수행되었다. 이후 우리나라의 벽식 구조 공동주택의 슬래브 구조 모델링과 주파수 응답 함수 연구를 통한 바닥충격음 예측에 대한 연구 결과(45,46)가 발표되었다. 구축된 예측 모델을 바탕으로 완충재가 적용된 경우 저주파 대역 중량충격음 증폭 현상(47)과 수음실에서의 음향 모드로 인한 중량충격음 특성(48)을 해석적으로 설명한 연구와 완충재가 적용된 뜬바닥 구조의 동특성에 대한 연구(49)도 수행되었다. 바닥충격음 예측을 위한 연구가 지속적으로 수행되었지만, 바닥충격음 성능이 우수한 공동주택 설계에 활용하기 위해서는 지속적인 후속연구와 예측 방법 표준화 등이 필요하다. 유럽 국가들은 경량충격음 뿐만 아니라, 공기전달음, 실내음향 특성 등에 대한 예측 방법을 수립하고 표준화하여 실제 다양한 건축물의 음향설계에 활용하고 있다. 또한 지속적으로 예측의 정확도 향상을 위한 연구도 꾸준히 추진하고 있다.
바닥충격음과 관련된 기타 연구로는 주거환경에서의 생활소음에 대한 감성적 반응 조사(50), 층간소음의 성가심과 생활감에 대한 설문조사 연구(51)와 바닥충격음에 대한 거주자 만족도 조사 결과(52)도 발표되었다. 공동주택 거주자의 층간소음 반응에 대한 연구가 일정한 주기로 조사되었지만, 서로 다른 연구 방법으로 추진되었다. 향후 동일한 연구 방법을 활용하여 주기적으로 조사하는 장기간에 걸친 거주자 반응 연구 등도 추진되어야 한다.
3.2 바닥충격음 학술발표 현황
바닥충격음에 대한 한국소음진동공학회 학술발표는 1990년 부터 시작되었으며, 2000년 부터 증가하기 시작하여 2019년 현재 327편의 학술발표가 이루어졌다. Table 3에서와 같이 학술발표는 게재된 논문보다 넓은 주제를 다루고 있었으며, 산/학/연 다양한 연구자가 발효하였다.
327편의 학술발표를 Table 4의 발표 주제별로 구분하여 Table 5에 정리하였다. 학술발표가 가장 활발히 이루어진 주제는 역시 동일하게 바닥충격음 저감구조에 대한 것으로 약 47.4 %를 차지하였다. 다음으로는 측정‧평가 방법에 대한 학술발표가 27.8 %였으며, 바닥충격음 특성 예측을 위한 특성조사와 예측방법 연구 등에 대한 학술발표가 10.4 %였다. 기타 발표 내용으로는 바닥충격음에 대한 청감, 설문조사와 민원, 제도 개선 등에 대한 것이었다.
Fig. 2는 연도별 학술발표 건수를 주제별로 구분하여 정리한 것이다. 학술발표에서 가장 많은 비중을 차지하고 있는 저감구조에 대한 것은 2004년 ~ 2005년 급증하였으며 2017년 이후 다시 증가하고 있다. 반면 측정, 평가 방법에 대한 학술발표는 2000년 편수의 차이는 있지만 꾸준히 발표되고 있다. 바닥충격음 예측 연구에 대한 학술발표는 2000년대 초에는 바닥충격음 에너지 전달 경로, 바닥 슬래브 특성 파악 위주로 진행되었으면 2010년 이후에는 슬래브의 충격 진동 특성 예측 등 다양한 구조에 대한 예측 연구 결과가 발표되고 있다.
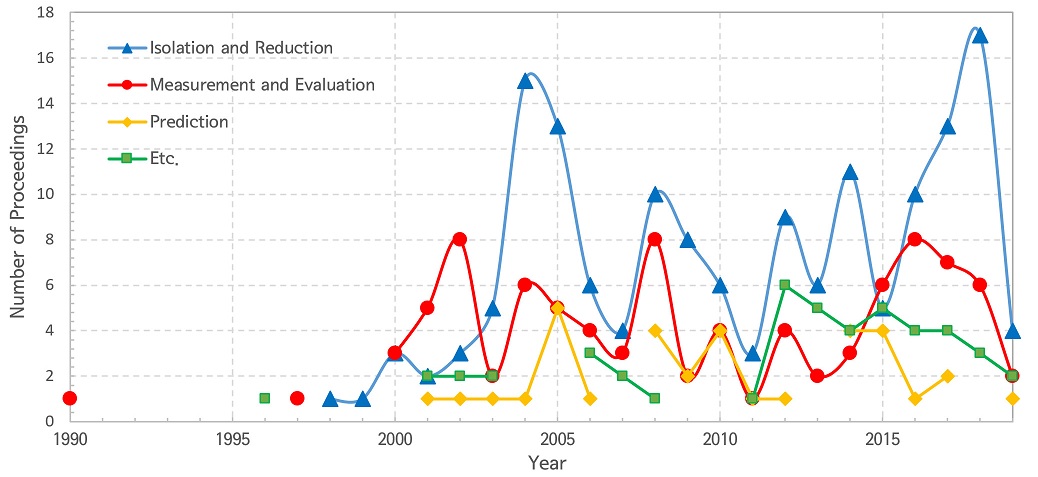
Number of papers and proceedings in each topic of floor impact sound from the 1990s to at present sorted by year
Table 6은 155편의 바닥충격음 저감구조에 대한 학술발표를 세부 주제별로 분류하여 정리한 것이다. 저감구조 관련 발표에서 뜬바닥 구조를 구성하는 완충재에 대한 발표가 가장 많았으며, 다음으로는 공동주택 구조개선, 마감재 순으로 나타났다. 보수 보강 기법과 리모델링 주택의 바닥충격음 차단성능 개선에 대한 발표는 2016년 이후 활발하게 발표되고 있다. 공동주택 바닥구조를 구성하는 구성층에 대한 다양한 결과가 발표되었으나, 저감구조 시공 품질관리 등에 대한 연구는 매우 부족한 것으로 나타났다.
Table 7은 바닥충격음 예측 방법에 대한 학술발표 34건을 세부 주제로 구분하여 정리한 것이다. 바닥충격음 예측과 관련하여 중량충격음에 대한 예측 방법이 주를 이루었으며, 우리나라 벽식 공동주택에서의 중량충격음 전달 특성 연구가 47.1 %로 가장 많았다. 다음으로는 공동주택 구조와 슬래브의 충격진동 특성 예측에 대한 것이 32.3 %, 공동주택 평면 차이에 의한 충격음 특성에 대한 발표는 5 %로 약 85 %의 예측 연구가 공동주택 충격음과 진동 전달 특성과 관련된 것을 알 수 있다. 완충재가 적용된 구조에 대한 모델링과 특성에 대한 연구는 3편만(2010년) 발표되었다. 향후 예측 기술과 관련해서는 공동주택 바닥 구조를 구성하는 각 구성층의 중량충격음 전달을 예측하기 위한 연구가 지속적으로 필요하며, 이를 바탕으로 중량충격음 예측 방법 표준화도 필요하다.
바닥충격음 측정, 평가 방법에 대한 학술발표는 91편이었으며, Table 8은 91편의 학술발표를 세부 주제별로 구분하여 정리한 것이다. 측정 방법에 대한 발표는 43편으로 47.3 %였으며, 표준 충격원에 대한 학술 발표가 가장 많았다. 다음으로는 바닥충격음 평가 방법에 대한 연구가 많았으며, 주로 청감평가와 단일수치평가량 연구 결과가 주를 이루었다. 또한 바닥충격음 저감을 위해 주로 사용되고 있는 완충재의 물성 측정 방법 개선을 위한 연구 결과 발표도 20.9 %를 차지하였다. Table 9는 기타 주제의 학술발표 47건을 세부 주제별로 구분하여 정리한 것으로, 민원관련 주제의 학술발표는 2012년부터 지속적으로 바닥충격음 민원실태, 층간소음 관리위원회 운영, 사회적 비용 등에 대하여 발표되고 있다.
4. 결 론
한국소음진동공학회가 창립된 이후 발표된 바닥충격음 관련 논문 및 학술발표를 정리하였다. 바닥충격음 주제의 논문은 40편이었으며, 학술발표는 327편(2019년도 춘계 소음진동학술대회까지)이 발표되었다. 한국소음진동공학회의 바닥충격음 관련 논문 및 학술발표 추세를 통해 보면, 우리나라의 바닥충격음 관련 연구는 1990년 후반부터 본격적으로 시작되었으며, 2000년을 기점으로 활발하게 연구되고 있다. 2005년 바닥충격음 차단성능 인정 제도에 따라 일시적으로 관련 발표가 감소하였지만, 이후 지속적으로 관련 연구결과가 발표되고 있다. 공동주택의 바닥충격음 관련 연구는 많이 수행되었지만 아직 연구, 개발해야 할 세부 분야가 많은 것으로 판단된다.
(1) 바닥충격음 논문의 주요 주제는 완충재를 포함하는 바닥충격음 저감구조, 측정‧평가 방법과 예측에 대한 논문이 주를 이루었다. 학술발표의 경우도 이와 유사하였으나, 바닥충격음 저감구조에 대한 비율이 더욱 높은 것으로 정리되었다. 이전의 바닥충격음 연구는 주로 완충재를 위주로 한 바닥충격음 저감 구조가 주를 이루었으며, 이는 과거 국토교통부가 바닥충격음 차단구조 인정 제도에서 제시한 표준바닥구조와 인정바닥구조가 완충재를 기반으로 한 뜬바닥 구조였기 때문으로 판단된다. 완충재에 대한 연구 주제는 연구개발뿐만 아니라 완충재의 물성 평가 방법에 대한 연구도 상당부분 발표되었다. 또한 공동주택의 바닥충격음 전달특성 파악과 구조 개선을 위한 바닥충격음 예측을 위한 연구도 2005년 이후 꾸준히 진행되고 있으며 공동주택의 바닥충격음 특성을 비교할 수 있는 수준으로 판단된다. 이외에 마감재, 모르타르, 천장 구조 등에 대한 연구도 수행되었다. 최근에는 층간소음 민원의 상당 부분을 차지하고 있는 기존 주택의 바닥충격음 차단성능 개선과 리모델링 시장 성장에 따라 여러 가지 설계, 시공 조건이 제한된 리모델링 공동주택의 바닥충격음 차단성능 개선에 대한 연구도 수행되고 있다.
현재까지의 우리나라의 바닥충격음 연구는 공동주택의 바닥충격음 전달 특성 파악, 바닥충격음 저감을 위한 완충재 위주의 연구개발이 주를 이루어왔다고 정리할 수 있다. 기타 주제의 연구 중에서는 바닥충격음 민원과 피해 금액 산정, 측정‧평가 방법의 국제표준화 등이 발표되었다.
(2) 바닥충격음 차단구조를 바닥 단면을 기준으로 봤을 때 바닥 마감재는 경량충격음 저감 성능 위주로 연구되어, 향후 기존 주택과 리모델링 주택에 적용할 수 있는 중량충격음 차단성능이 우수한 마감재 개발이 필요하며, 이와 함께 보행감 개선에 대한 연구도 함께 고려되어야 할 것으로 판단된다. 모르타르 및 단열층(경량기포 콘크리트)의 경우는 해당 자재의 물성 변화에 따른 바닥충격음(중량) 차단성능 변화에 대한 기초 자료 구축과 함께 현장에서 일정한 성능 확보를 위한 품질관리 방안 연구도 함께 제시될 필요가 있다. 완충재의 경우 다양한 완충재가 개발되고 많은 연구 결과가 발표되었지만, 각 공동주택 평형 및 평면별 특성에 따라 최적의 완충재를 선정하여 적용하는 기법 개발과 시공 품질 관리 방안 등에 대한 연구가 필요하다. 공동주택 슬래브에 대해서는 기존에 수행된 바닥충격음 특성 파악과, 예측 연구를 바탕으로 표준화된 공동주택 구조(슬래브 자체)의 중량충격음 레벨 예측 방법을 수립하는 것이 시급하다. 이를 통해 공동주택 평면과 구조 설계시 바닥충격음 차단 성능이 우수한 구조시스템을 제안할 수 있으며, 다양한 구조 설계인자가 바닥충격음 차단성능에 미치는 영향을 정량적으로 비교할 수 있을 것이다. 또한 각 세대별 균일한 바닥충격음 레벨 확보를 위한 현장에서의 구조 시공 품질 관리 기법 개발 등의 기초 자료로 활용할 수 있다. 천장 구조에 대한 개발은 현재 활발하게 수행되고 있으며, 천장 내부 공간의 흡음 성능 개선과 밀폐된 천장 내부 공간으로 인한 공명현상 개선에 대한 연구가 진행되었다. 그러나 천장 마감재료와 시공 구조는 기존 시스템을 기반으로 하고 있어, 향후 다양한 재료와 저주파 충격진동을 효과적으로 차단할 수 있는 설치 구조 등에 대한 연구도 필요한 것으로 판단된다.
(3) 바닥충격음 표준기반과 관련 제도에 대하여서는 현재 추진되고 있는 중량충격음(볼) 평가 방법 및 평가 등급에 대한 국제표준 발간이 시급하며, 이와 함께 중량충격음(볼) 간이 측정법을 국제표준에 추가하는 것이 필요하다. 중량충격음(볼) 간이 측정 방법은 현장에서의 품질관리 기법 개발을 위한 기초 자료 조사에 유용하게 활용될 수 있을 것으로 판단되며, 향후 간이 측정 방법과 최종 현장측정 결과 사이의 상관성, 정확도 등에 대한 연구 결과도 제시되어 할 것으로 판단된다. 바닥충격음과 공동주택 음향 성능 표시 방법(ISO/TS 19488)에 대한 검토가 필요하며, 공동주택 건설 이후 사후 측정을 위한 샘플링 기법, 성능 편차 등에 대한 조사 결과 제시도 필요하다. 또한 해당 국제표준의 KS 부합화와 함께 민간 주도의 공동주택 음향 성능 표시제도 등에 대한 논의도 필요한 것으로 판단된다. 성공적인 음향 성능 표시제도가 되기 위해서는 각 음향 성능 등급별로 제시된 수준을 입주자가 충분히 이해할 수 있어야 한다. 이를 위해서는 국제표준안에 제시된 각 음향 성능별 입주자 만족도에 대한 검증 연구가 필요한 것으로 사료된다. 입주자 만족도 검증을 위한 연구 방법으로는 실제 공동주택 또는 이와 유사한 환경에서의 각 음향 성능별 청감실험과 대규모 설문조사 및 음향 성능 측정이 필요하다. 실제 거주 공동주택을 대상으로 하는 대규모 설문조사와 측정 결과가 가장 설득력이 있고 신뢰성이 높은 결과지만 많은 시간과 노력, 비용이 필요하기 때문에 실제 수행하기에는 어려운 점이 많은 것으로 판단된다.
(4) 이외에 바닥충격음 관련 연구 주제로는 입주자의 소음 민감도와 만족 수준, 바닥충격음에 대한 우리 신체가 반응하는 특성 등에 대한 정량적인 수치화 연구가 향후 필요할 것으로 사료된다. 이상과 같이 과거 바닥충격음 관련 연구가 활발하고 지속적으로 추진되어 왔으나, 앞으로 중량충격음 예측 기술, 저주파 충격음 차단 구조 개발과 시공 품질관리 방안과 바닥 저감 기술의 가치 평가 등 연구하여야 할 다양한 주제가 많은 것으로 판단된다. 또한 연구결과를 표준화하고 관련 정책 등에 반영하는 것이 필요하다.
References
- Korea Environment Corporation, Floor Impact Sound Call Center August and September 2018 Report, 2018. 11.
- KS F 2810, (1996), Field Measurements of Impact Sound Insulation of Floors.
- KS F 2810-1, (2015), Field Measurements of Impact Sound Insulation of Floors-Part 1: Method Using Standard Light Impact Source.
- KS F 2810-2, (2012), Field Measurements of Floor Impact Sound Insulation of Buildings―Part 2: Method Using Standard Heavy Impact Sources.
- ISO 12354-2, (2017), Building Acoustics―Estimation of Acoustic Performance of Buildings from the Performance of Elements―Part 2: Impact Sound Insulation between Rooms.
- ISO 10848-1, (2017), Acoustics―Laboratory and Field Measurement of Flanking Transmission for Airborne, Impact and Building Service Equipment Sound between Adjoining Rooms―Part 1: Frame Document.
- ISO 10848-2, (2017), Acoustics―Laboratory and Field Measurement of Flanking Transmission for Airborne, Impact and Building Service Equipment Sound between Adjoining Rooms―Part 2: Application to Type B Elements when the Junction Has a Small Influence.
- ISO 10848-3, (2017), Acoustics―Laboratory and Field Measurement of Flanking Transmission for Airborne, Impact and Building Service Equipment Sound between Adjoining Rooms―Part 3: Application to Type B Elements when the Junction Has a Substantial Influence.
- ISO 10848-4, (2017), Acoustics―Laboratory and Field Measurement of Flanking Transmission for Airborne, Impact and Building Service Equipment Sound between Adjoining Rooms―Part 4: Application to Junctions with at least One Type A Element.
- ISO/TS 19488, (2019), Acoustics―Acoustic Classification of Dwellings.
- Kim, S.-W., Son, C.-B., and Jang, G.-S., (1990), A Study on the Evaluation Method of Impact Sound for Apartment House, Proceedings of the KSNVE Annual Autume Conference, p149-154.
- Kim, K. W., Choi, G. S., Choi, H. J., and Yang, K. S., (2004), Evaluation of Floor Impact Sound Performance according to the Reduction Methods, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 14(9), p811-818.
- Kim, K. W., Kang, J. S., Lee, S. E., and Yang, K. S., (2005), Floor Impact Sound Isolation Performance by Composition of Ceiling and Wall, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 15(4), p465-473.
- Kim, K. W., Jeong, G. C., and Sohn, J. Y., (2008), Evaluation of the Dynamic Stiffness and Heavy-weight Floor Impact Sound Reduction by Composition of Resilient Materials, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 18(2), p247-254.
- Kim, K. W., Jeong, G. C., and Sohn, J. Y., (2008), Correlation between Dynamic Stiffness of Resilient Materials and Lightweight Floor Impact Sound Reduction Level, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 18(8), p661-667.
-
Kim, J. H., Mun, D. H., Jeong, G. C., and Park, H. G., (2017), Influence of Floor Dimension and Resilient Material on Heavy Impact Nosie of Floating Floor System, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 27(4), p434-443.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/ksnve.2017.27.4.434]

-
Song, G. G., Kim, Y. H., Ryu, J. K., and Kim, M. J., (2018), Analysis of Heavyweight Floor Impact Sound Level with Dynamic Stiffness and Thickness of EPS Type Resilient Materials, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 28(6), p713-720.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/ksnve.2018.28.6.713]

- Seo, S. H., Song, H. S., and Jeon, J. Y., (2004), Noise and Vibration Characteristics of Concrete Floor Structures Using Resilient Materials Driven by Standard Heavy Impact Source, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 14(8), p661-667.
- Jeong, Y., and Jeon, J. Y., (2006), Vibration Characteristics of the Floor Structures Inserted with Damping Materials, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 16(10), p1036-1043.
-
Yun, C. Y., Jeong, J. H., and Kim, M. J., The Effect of Aerated Concrete Containing Foam Glass Aggregate on the Floor Impact Sound Insulation, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 23(5), p414-422.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/ksnve.2013.23.5.414]

-
Mun, D. H., Oh, Y. G., Jeong, G. C., and Park, H. G., (2016), Floor Impact Noise Level for Concrete Slab Integrated with Floor Finishing Layers, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 26(2), p130-140.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/ksnve.2016.26.2.130]

-
Yun, C. Y., Yeon, J. O., and Kim, M. J., (2014), Comparison of Impact Sound Insulation Performances of Apartment Floor Against Heavy-weight Impact Sources via Field Measurement Data, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 24(8), p651-658.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/ksnve.2014.24.8.651]

- Chung, H. W., Gi, N. G., Song, M. J., and Kim, S. W., (2002), A Study on the Reduction Characteristics of Floor Impact Sound Insulation Due to the Ceiling Frame Structures in Apartment Houses, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 12(8), p573-580.
-
Yeon, J. O., Kim, K. W., Choi, H. J., Yang, G. S., and Kim, K. H., (2013), Experiment Evaluation for the Heavy-weight Impact Sound of Dry Double-floor System - Effect of Rubber Hardness and Ceiling Structure -, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 23(1), p34-40.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/ksnve.2013.23.1.034]

-
Mun, D. H., Song, G. G., Lee, C. S., and Park, H. G., (2014), Reduction of Floor Impact Nosie and Impact Force for PVC Floor Covering and Floor Mat, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 24(7), p501-508.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/ksnve.2014.24.7.501]

- Kim, K. W., Choi, G. S., Jeong, Y. S., Yang, K. S., (2005), Impact Power Characteristics as Behavior or Real Impact Source(Child), Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 15(5), p542-549.
- Jeon, J. Y., Lee, P. J., Jeong, J. H., and Part, J. H., (2006), Comparison of Standard Floor Impact Sources with a Human Impact Source, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 16(8), p789-796.
- Jeong, J. H., and Jeon, J. Y., (2005), Floor Impact Noise Measurement and Evaluation Method Using Impact Ball, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 15(10), p1160-1168.
-
Park, H. K., Kim, K. M., and Kim, S. W., (2013), Verification of Effectiveness of the Standard Floor Impact Source by Comparing with Living Impact Sources, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 23(12), p1117-1126.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/ksnve.2013.23.12.1117]

- Lee, J. W., and Kwon, Y. P., (2006), Effect of the Measuring Method of Reverberation Time Using Impulse Response Method on the Normalized Impact Sound Pressure Level, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 16(1), p34-39.
-
Jeong, J. H., Kim, J. U., and Jeong, J. G., (2013), Floor Impact Sound Pressure Level Characteristics by the Change or Reverberation Time in a Reverberation Chamber, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 23(3), p274-281.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/ksnve.2013.23.3.274]

- Joeng, J. H., Lee, B. K., Yeon, J. O., and Jeon, J. Y., (2014), Floor Impact Sound Pressure Level Characteristics by the Change or Reverberation Time in Mock-up Test Rooms, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 24(4), p339-347.
-
Jeong, J. H., (2018), Effect of Directivity and Position of Sound Source when Measure Reverberation Time for the Correction of Receiving Room, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 28(4), p388-396.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/ksnve.2018.28.4.388]

- Jeon, J. Y., and Ryu, J. K., (2006), A Combined Rating System for Multiple Noises in Residential Buildings, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 16(10), p1005-1013.
- Shin, H., Kim, S. W., and Jang, G. S., (2009), Subjective Assessment of Simulated Heavy Floor Impact Sounds for Alternative Rating Method, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 19(3), p282-287.
- Yoo, S. Y., Yeon, J. O., and Jeon, J. Y., (2009), Analysis and Evaluation of Impact Sound Insulation of Concrete Floor Structures in Responses to Characteristics of Heavy-weight Impact Sources, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 19(10), p1062-1068.
-
Lee, M. J., and Choi, H. K., (2017), Characteristics of Transmission of Floor Vibration and Floor Impact Noise Due to Human Activities, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 27(1), p5-13.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/ksnve.2017.27.1.005]

-
Kim, K. W., Yeon, J. O., and Yang, K. S., (2012), Correspondence Research of Long-term Compressive Creep of Resilient Materials and ISO 20392, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 22(12), p1250-1256.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/ksnve.2012.22.12.1250]

- Chung, J. Y., (2009), Small-size Specimen's Effectiveness That Is Used to Mortar Layer of Slab(Heavy-weight Floor Impact Sound), Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 19(2), p184-191.
- ISO 12354-3, (2017), Building Acoustics―Estimation of Acoustic Performance of Buildings from the Performance of Elements―Part 3: Airborne Sound Insulation against Outdoor Sound.
- Kim, M. J., Kim, H. S., and Kim, H. G., (2003), Prediction of Floor Impact Sound by Measuring the Vibration Acceleration Level on the Interior Structures of Receiving Room in Apartment Buildings, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 13(1), p3-9.
- Kim, H. G., Kim, M. J., and Oh, Y. K., (2003), Assessment of Vibration Transmissibility for Prediction of Heavy Floor Impact Sound, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 13(6), p415-422.
- Seo, S. H., and Jeon, J. Y., (2005), 2-dimensional Floor Impact Vibration Analysis in Bare Reinforced Concrete Slab Using Finite Element Method, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 15(5), p604-611.
-
Yoo, S. Y., and Jeon, J. Y., (2011), Experimental Studies for Analysing of Characteristics of Floor Impact Sound through a Scale Model with Box-frame Type Structure, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 21(9), p805-812.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/ksnve.2011.21.9.805]

- Hwang, J. S., Mun, D. H., Park, H. G., Hong, S. G., and Hong, G. H., (2009), The Numerical Analysis of Heavy Weight Impact Noise for an Apartment House, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 19(2), p162-168.
-
Mun, D. H., Park, H. G., and Hwang, J. S., (2014), Prediction of Concrete Slab Acceleration and Floor Impact Noise Using Frequency Response Function, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 24(6), p483-492.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/ksnve.2014.24.6.483]

-
Moon, D. H., Park, H. G., Hong, S. G., and Hong, G. H., The Effect of Dynamic Property of Absorbing Sheet on the Amplification of Heavy Weight Floor Impact Noise, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 20(7), p651-657.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/ksnve.2010.20.7.651]

-
Mun, D. H., Park, H. G., Hwang, J. S., Hong, G. H., and Im, J. H., (2012), Numerical Analysis of Heavy-weight Impact Noise for Apartment Units Considering Acoustic Mode, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 22(7), p676-684.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/ksnve.2012.22.7.676]

-
Mun, D. H., Park, H. G., Hwang, J. S., and Hong, G. H., (2014), An Analysis of Characteristics of Floor Dynamic Properties and Bang-machine Impact Force on Floating Floor Using System Analysis, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 24(5), p390-398.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/ksnve.2014.24.5.390]

- Jeon, J. Y., Kim, K. H., Jeong, J. H., Ryu, J. K., and Cho, M. J., (2002), Perceptual Evaluation of Noise Sources in a Chamber for Residential and Working Environment, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 12(6), p437-444.
-
Kim, K. W., Choi, H. J., Kim, Y. S., and Yang, K. S., (2010), Investigation Research on the Residents Satisfaction Rating to the Floor Impact Sound in Apartment Buildings, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 20(2), p179-184.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/ksnve.2010.20.2.179]

-
Jeong, J. H., and Lee, P. J., (2018), Questionnaire Survey on Annoyance and Disturbance of Floor Impact Sound, Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 28(6), p685-693.
[https://doi.org/10.5050/ksnve.2018.28.6.685]


JeongHo Jeong is currently a senior researcher at Fire Insurers Laboratories of Korea(FILK). He received his M.S. and Ph.D. degree in architectural engineering from Hanyang University, Korea. His research is interests include standardization in building acoustics field. Also, he has interest on the sound localization research for AES(acoustic evacuation signal).